
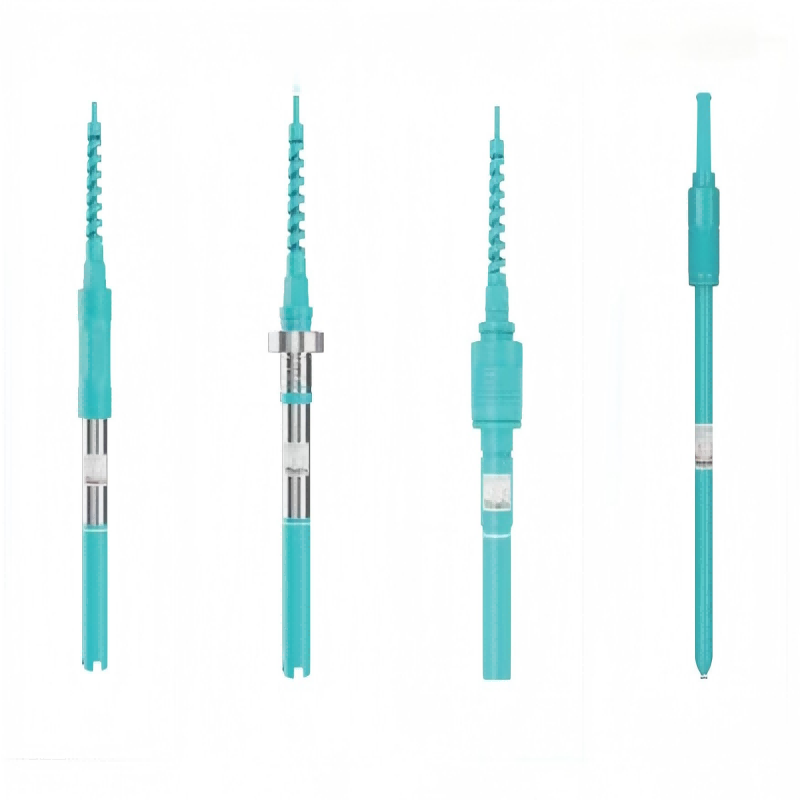


Inquiry
(1)Conductivity is a parameter used to describe the ease with which electric charge flows through a substance. In formulas, conductivity is denoted by the Greek letter σ. The standard unit of conductivity σ is Siemens per meter (abbreviated as S/m), which is the reciprocal of resistivity ρ, i.e., σ = 1/ρ. When a current of 1 Ampere (1 A) passes through the cross-section of an object with a voltage of 1 Volt (1 V), the conductance of the object is 1 Siemens. The Siemens is essentially equivalent to 1 Ampere per Volt. If G is the conductance (in Siemens), I is the current (in Amperes), and U is the voltage (in Volts), then: G = I/U. The conductivity σ can be calculated from the conductance G, the cross-sectional area A of the conductor, and the length l of the conductor: σ = Gl/A.
(2) Measurement Principle: The measurement principle of conductivity involves placing two parallel plates (or cylindrical electrodes) with a fixed distance L into the solution to be measured, and applying a certain potential difference across the plates (to avoid electrolysis of the solution, a sinusoidal voltage with a frequency of 1–3 kHz is typically used). The conductance between the plates is then measured by a conductometer.
Measuring conductivity requires two pieces of information: the conductance G of the solution and the cell constant Q of the conductance cell. The conductance can be obtained by measuring the current and voltage.
The value of conductivity is obtained from the relationship K = Q × G. This measurement principle is widely used in direct-reading measuring instruments.
(3) Measurement Methods: Conductivity measurement typically refers to the measurement of the conductivity of solutions. The resistivity of solid conductors can be measured using Ohm's law and the resistance law. For electrolyte solutions, the conductivity is generally measured by applying an alternating current signal to the two electrodes of a conductance cell, and calculating the conductivity σ from the measured cell constant K and the conductance G between the two electrodes.
The earliest method used for conductivity measurement was the AC bridge method, which directly measures the conductance value. The most commonly used instrument settings include a constant regulator, a temperature coefficient regulator, and an automatic temperature compensator. The primary instrument section consists of a conductance cell and a temperature sensor, which can directly measure the conductivity of electrolyte solutions.
Ultra-pure water, pure water, drinking water, sewage, aquaculture, boiler water, circulating water, river monitoring, industrial water, cooling water, wastewater treatment, electric power, chemical industry, pharmaceutical industry, food, surface water, reverse osmosis, seawater desalination, water treatment, etc.

All products purchased from our company will receive free installation guidance and product training; The free warranty period is 1 year.
All products purchased from our company will receive free installation guidance and product training; The free warranty period is 1 year.

All products purchased from our company will receive free installation guidance and product training; The free warranty period is 1 year.
All products purchased from our company will receive free installation guidance and product training; The free warranty period is 1 year.


